Abstract
In multiple myeloma (MM), whole exome sequencing (WES) studies have revealed four mutational signatures: two associated with aberrant activities of APOBEC cytidine deaminases (Signatures #2 and #13) and two clock-like signatures associated with "cancer age" (Signatures #1 and #5). Mutational signatures have not been investigated systematically in larger series, nor in other primary plasma cell dyscrasias such as monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) or primary plasma cell leukemia (pPCL). Finally, while APOBEC activity has been correlated to increased mutational burden and poor-prognosis MAF/MAFB translocations in MM at diagnosis, this has never been confirmed in multivariate analysis in an independent series.
To answer these questions, we mined 1151 MM samples from public WES datasets, including samples from the IA9 public release of the CoMMpass trial. The CoMMpass data were generated as part of the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation Personalized Medicine Initiatives. We also analyzed 6 MGUS/Smoldering MM as well as 5 previously published pPCLs. Extraction of mutational signatures was performed using the NNMF algorithm as previously described (Alexandrov et al. Nature 2013).
NNMF in the whole cohort extracted the known 4 signatures pertaining to distinct mutational processes: the two clock-like processes (signatures #1 and #5) and aberrant APOBEC deaminase activity (signatures #2 and #13). While the clock-like processes were more prominent in the cohort as a whole (median 70%, range 0-100%), the APOBEC showed a heterogeneous contribution, more visible in samples with the highest mutation burden. In fact, the absolute and relative contribution of APOBEC activity to the mutational repertoire correlated with the overall number of mutations (r=0.71, p= < 0.0001). As previously described, APOBEC contribution was significantly enriched among MM patients with t(14;16) and with t(14;20) (p<0.001), but the association between relative APOBEC contribution and mutational load remained significant across all cytogenetic subgroups with the exception of t(11;14). In the MGUS/SMM series, APOBEC contribution was generally low. Conversely, APOBEC activity was preponderant in three out of five pPCL samples, all of them characterized by the t(14;16)( IGH / MAF); in the remaining two pPCL the absolute number of APOBEC mutations was similar to MM. Overall, the APOBEC contribution was characterized by a progressive increment from MGUS/SMM to MM and pPCL.
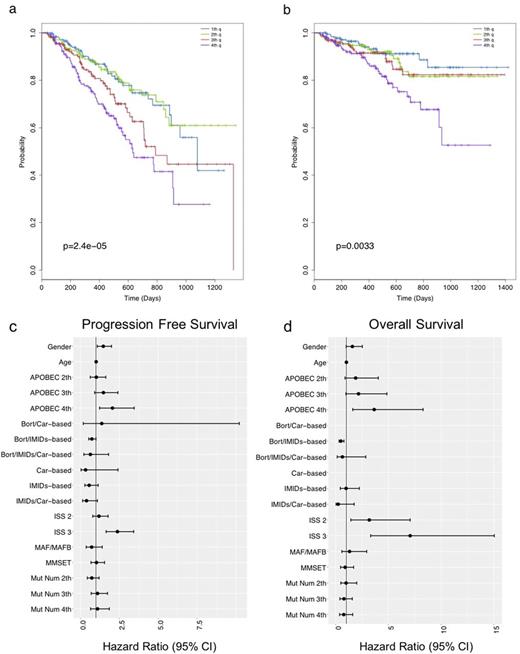
We next went on to investigate the prognostic impact of APOBEC signatures at diagnosis. Patients with APOBEC contribution in the 4th quartile had shorter PFS (2-y PFS 47% vs 66%, p<0.0001) and OS (2-y OS 70% vs 85%, p=0.0033) than patients in quartiles 1-3 (Figure 1a-b). This was independent from the association of APOBEC activity with MAF translocations and higher mutational burden, as shown by multivariate analysis with Cox regression (Figure 1c-d). ISS stage III was the only other variable that retained its independent prognostic value for both PFS and OS. We therefore combined both variables and found that co-occurrence of ISS III and APOBEC 4th quartile identifies a fraction of high-risk patients with 2-y OS of 53.8% (95% CI 36.6%-79%), while their simultaneous absence identifies long term survivors with 2-y OS of 93.3% (95% CI 89.6-97.2%).
In this study, we provided a global overview on the contribution of mutational processes in the largest whole exome series of plasma cell dyscrasias investigated to date by NNMF. We propose that cases with high APOBEC activity may represent a novel prognostic subgroup that is transversal to conventional cytogenetic subgroups, advocating for closer integration of next-generation sequencing studies and clinical annotation to confirm this finding in independent series.
Corradini: Amgen: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria. Anderson: Oncopep: Other: scientific founder; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millenium Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MedImmune: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; C4 Therapeutics: Other: scientific founder. Avet-Loiseau: Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene, Janssen: Research Funding; Janssen, Sanofi, Celgene, Amgen: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal